The C1815 transistor, also known as 2SC1815, stands as a versatile component in contemporary electronics, prized for its application in both amplification and switching circuits. With capabilities suited to handling moderate voltages and currents, it finds extensive use in audio amplifiers, signal processing modules, and various other electronic devices. This transistor's robust performance characteristics, including low noise operation and reliable hFE linearity, underscore its pivotal role in delivering high-quality audio output and facilitating efficient signal processing across a spectrum of applications.

C1815 Transistor Overview
The C1815, also known as 2SC1815, is an NPN bipolar junction transistor widely utilized in various electronic applications. It functions as both an electronic switch and an amplifier, controlling the flow of current through circuit paths based on input voltage or current. Designed for audio frequency amplification and high-frequency oscillation, the C1815 can handle collector-base voltages up to 50V and collector currents up to 150mA, making it suitable for circuits operating under 50V DC. Its low noise operation and excellent hFE linearity make it ideal for audio amplification and signal processing.
This transistor has a current gain (hFE) ranging from 70 to 700, with specific classifications: C1815O (70-140), C1815Y (120-240), C1815GR (200-400), and C1815BL (350-700). The C1815’s good power dissipation capabilities and versatility in driving loads under 150mA make it a popular choice for both commercial and educational projects. Its reliable performance in audio and high-voltage applications underscores its importance as a fundamental component in modern electronics.
C1815 Transistor Pinout
The C1815 transistor, like most transistors, has three pins: the base (B), collector (C), and emitter (E). Understanding the function of each pin is essential for properly integrating the transistor into electronic circuits.
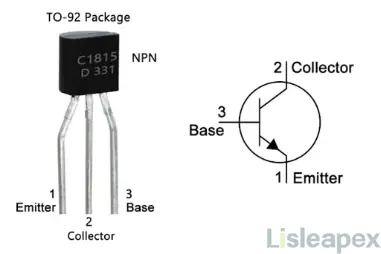
Pin Descriptions:
- Emitter (E): The emitter serves as the primary current flow path along with the collector. Typically, it is connected to a negative or ground voltage, facilitating the current exit from the transistor.
- Collector (C): The collector is a key terminal in the main current flow, regulated by the base. It is usually connected to a positive voltage, allowing it to collect the charge carriers flowing through the transistor.
- Base (B): The base acts as the control terminal of the transistor. A small current introduced at the base regulates a much larger current flow between the collector and emitter. This control mechanism is fundamental to the transistor's ability to function as an amplifier or switch.
C1815 Transistor Uses & Application
Where to use C1815 Transistor
The C1815 transistor is ideal for various applications, including audio amplification, signal processing, and switching tasks. Its low noise operation and high-frequency capabilities make it suitable for use in audio equipment, preamplifiers, and small audio amplifiers. Additionally, it can efficiently drive loads under 150mA, making it useful in a range of electronic circuits, from simple switching tasks to more complex configurations like Darlington pairs.
Applications of C1815
- Sensor Circuits: Used to amplify weak signals from sensors before further processing or measurement.
- Audio Preamplifiers: Employed in the initial amplification stage of audio equipment to boost low-level audio signals without adding significant noise.
- Audio Amplifier Stages: Integral in both the intermediate and final stages of audio amplifiers to ensure adequate amplification and signal integrity.
- Switching Loads Under 150mA: Used to control and drive loads such as relays, small motors, or LEDs in various electronic projects and devices.
- RF Circuits: Utilized in radio frequency applications for tasks like oscillation, amplification, and modulation due to its high conversion frequency.
- Push-Pull Configuration Circuits: Applied in push-pull amplifier configurations to improve efficiency and reduce distortion in audio signals.
- Driver Stage Amplifiers: Functions as a driver transistor in amplifier circuits to provide sufficient current and voltage to subsequent stages or loads.
How to Test C1815 Transistor
Step1. Identify Pins:
Locate the pins on the C1815 transistor: Emitter (E), Base (B), and Collector (C).
Step2. Set Multimeter:
Turn on your digital multimeter and set it to the diode test mode (usually denoted by a diode symbol).
Step3. Test Emitter-Base Junction:
- Place the black probe (negative) of the multimeter on the Emitter (E) pin of the transistor.
- Touch the red probe (positive) to the Base (B) pin.
- Look for a voltage drop reading on the multimeter. You should see a voltage drop of approximately 0.6V to 0.7V, indicating a forward-biased junction.
By following these three steps, you can check the basic functionality of the C1815 transistor and verify its proper operation in a circuit. For further testing, such as checking the Emitter-Collector junction or using the hFE mode for gain measurement, additional steps and configurations on the multimeter may be required.
C1815 Transistor Amplifier Circuit Diagram
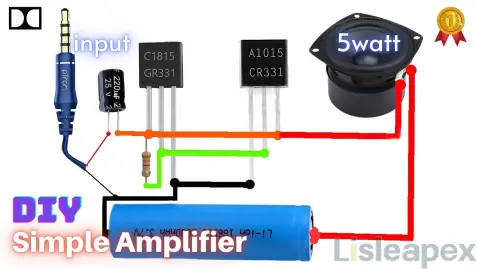
Here's the video about C1815 transistor amplifier circuit,
Advantages and Disadvantages of C1815 Transistor
The C1815 transistor offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice in various electronic applications. Its strengths lie primarily in its suitability for audio amplification and moderate-power circuitry.
Advantages:
- Low Noise Operation: The C1815 transistor excels in applications requiring minimal noise, such as audio amplification. Its low noise characteristics ensure clear and high-quality audio output.
- Excellent hFE Linearity: It provides precise amplification with consistent hFE (current gain) linearity across different operating conditions. This feature is crucial for faithful signal reproduction in audio circuits.
- High Voltage and Current Handling: Capable of handling relatively high voltages and collector currents, the C1815is suitable for power conditioning circuits where robust performance is required.
- High Conversion Frequency: Its high conversion frequency enables efficient operation at elevated frequencies, expanding its utility in radio frequency (RF) applications and high-frequency signal processing.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Power Dissipation Capability: Despite its ability to handle high voltages, the C1815has constraints on power dissipation. This limits its suitability for applications demanding very high power outputs.
- Not Suitable for Very High-Speed Switching: It may not be ideal for circuits requiring extremely rapid switching or operation at frequencies beyond its transition frequency limits. Applications needing ultra-high-speed performance may require alternative transistors.
- Availability Considerations: While widely available, regional shortages or specific application needs may necessitate using equivalent transistors due to supply chain factors or component availability issues.
C1815 Transistor Equivalent and Replacement
When the C1815 transistor is unavailable or unsuitable for a specific application, several equivalent parts can serve as suitable replacements. These alternatives share comparable electrical characteristics and functionalities, making them compatible substitutes in most circuit designs.
| Equivalent Transistors | Description |
|---|---|
| 2N5088 | General purpose NPN transistor with low noise and high gain, ideal for audio and general amplification. |
| BC549 | Low-noise, low-signal NPN BJT transistor commonly used in audio amplifiers and signal processing applications. |
| BC107 | General purpose NPN transistor suitable for low-power audio applications and signal amplification. |
| 2N2222 | Versatile and rugged NPN transistor widely used in various electronic circuits for switching and amplification. |
| BC547 | Popular NPN transistor known for general purpose switching and amplification in electronic circuits. |
Additional Equivalents:
- 2SC2458, 2SC3198, 2SC3199, 2SC3916, 2SC3917, 2SC3918, 2SC3919, 2SC3920, 2SC3921, 2SC3922, 2SC3923, C945, KSC1815, KSC945C, KTC3198, KTC3199
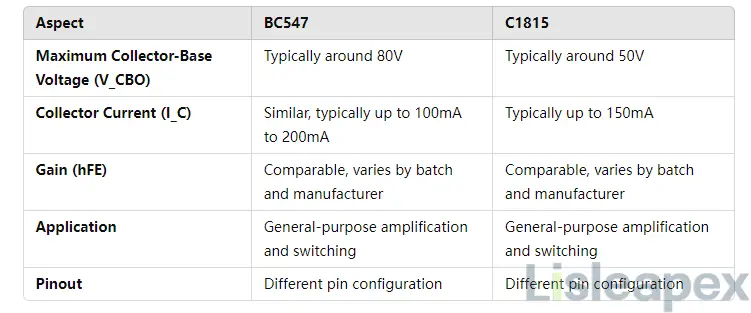
Differeneces between BC547 and C1815
The BC547 and C1815 transistors, both NPN bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), share similarities in their applications for amplification and switching. However, they differ in several key aspects related to their electrical characteristics and maximum ratings.
While both the BC547 and C1815are NPN BJTs suitable for general-purpose circuits, they vary notably in maximum voltage ratings and specific application scenarios.
Detailed Comparison:
Is C1815 Compatible with BC547 Transistor
Yes, the C1815and BC547 transistors are generally compatible for most common electronic circuits. They both operate as NPN BJTs suitable for amplification and switching applications, with similar collector current capabilities. However, designers should verify specific electrical characteristics such as maximum voltage ratings and pin configurations to ensure proper functionality and reliability when substituting one for the other in a circuit.
C1815 Transistor Package
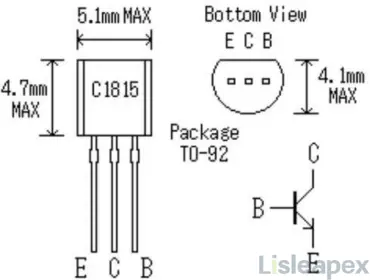
C1815 Transistor Datasheet PDF
Download C1815 Transistor Datasheet PDF here>>
Conclusion
In conclusion, the C1815 transistor remains a cornerstone in electronic design, offering engineers and enthusiasts alike a dependable solution for amplification and switching needs. Despite considerations such as voltage ratings and pin configurations when compared to counterparts like the BC547, its widespread availability and adaptability make it a preferred choice in diverse electronic projects. As technology advances, the C1815 transistor continues to prove its enduring relevance and reliability, ensuring it remains integral to the evolution of modern electronic circuits and applications.
FAQ
-
Can the C1815 transistor be used as a switch?
Yes, the C1815 transistor can function as an electronic switch. By applying a small current to the base, it can control a larger current flow from the collector to the emitter, allowing it to turn on or off circuit paths in electronic devices.
-
What are the typical operating conditions for the C1815 transistor?
The C1815 transistor is typically operated under conditions where the collector-base voltage (V_CBO) does not exceed 50V and the collector current (I_C) remains within the range of 150mA. It is often used in circuits powered by DC voltages up to 50V.
-
In what types of circuits is the C1815 transistor commonly used?
The C1815 transistor is commonly used in audio amplification circuits, such as in preamplifiers and small audio amplifiers, where low noise and accurate signal amplification are crucial. It is also found in sensor circuits, RF circuits for oscillation and amplification, and various switching applications.
-
What is the thermal performance of the C1815 transistor?
It has a maximum power dissipation (P_D) rating, typically around 400mW. Proper heat sinking or thermal management is important to ensure the transistor operates within safe temperature limits, which can affect its longevity and reliability in circuits.
-
Can the C1815 transistor be used in high-frequency applications?
Yes, the C1815 transistor has a high conversion frequency, making it suitable for applications requiring operation at elevated frequencies. It can be used in RF circuits for tasks such as modulation, amplification, and signal processing up to its maximum frequency capabilities.
Stay updated with Lisleapex by signing up for the newsletter


 Congratulations On Your Successful Submission
Congratulations On Your Successful Submission
 Submission Failure
Submission Failure
