Difference between Single Power Supply and Dual Power Supply
A single power supply refers to a power source that provides only either the positive or negative voltage after rectification. For example:

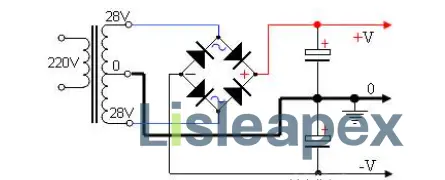
A dual power supply refers to a power source that is simultaneously supplied with both positive and negative voltages. For example:
Operational amplifiers, as one of the primary components in analog circuits, can be powered either by a single power supply or a dual power supply. Choosing the appropriate power supply configuration can be confusing for beginners. I have conducted detailed experiments to address this issue, and I will provide a summary.
Firstly, operational amplifiers are classified into single power supply operational amplifiers and dual power supply operational amplifiers. In the datasheet of an operational amplifier, if the power supply voltage is specified as (+3V-+30V)/(±1.5V-±15V), such as LM324, it indicates a single power supply operational amplifier that can be powered by either a single power supply or a dual power supply. If the power supply voltage is specified as (±1.5V-±15V), such as LM741, it indicates a dual power supply operational amplifier that can only be powered by a dual power supply.
However, in practical applications, both types of operational amplifiers can be powered in either single power supply or dual power supply mode. The specific usage is as follows:
1. When amplifying DC signals, if a dual power supply operational amplifier is used, it is preferable to choose a positive and negative dual power supply. Otherwise, when the input signal amplitude is small, the operational amplifier may not function properly. If a single power supply operational amplifier is used, it can work correctly with either a single power supply or a dual power supply.
2. When amplifying AC signals, both single power supply operational amplifiers and dual power supply operational amplifiers can function properly with a positive and negative dual power supply.
3. When amplifying AC signals, neither single power supply operational amplifiers nor dual power supply operational amplifiers can work correctly with a simple single power supply. In the case of single power supply operational amplifiers, this manifests as the inability to amplify the negative half-cycle of the signal, while dual power supply operational amplifiers fail to function properly.
To use a single power supply, a so-called "biasing" is required. The result of biasing is transforming the relative single power supply into a "dual power supply" configuration.
Differences between Dual Loop and Dual Power Supply
Dual loop power supply generally refers to a power source with two loops for a particular load. This power source is connected to different switches in the upstream distribution. During normal operation, one loop supplies power while the other loop remains in standby. When one loop experiences a power outage, the user-side automatic switching device switches the power source, ensuring uninterrupted power supply to the load.
Dual power supply typically refers to two power sources originating from different substations (or distribution centers) to prevent simultaneous voltage loss in both power sources. This configuration is commonly used for supplying power to critical users such as airports, train stations, hospitals, etc. (these locations often have their own power generation capabilities as well).
Dual power supply and dual loop power supply are generally considered synonymous and are often used interchangeably. However, there are some differences between them. Dual power supply refers to sourcing power from two distinct power sources (with different characteristics), and it involves two power supply lines. If the term "one primary and one backup" refers to the power source, then it can be considered a dual power supply. However, if it refers to the power feed lines, it cannot be referred to as dual power supply.
Dual power supply is more reliable than dual loop power supply. However, from the perspective of a building or facility, they may appear similar since both often involve two incoming power lines. In one scenario of dual power supply, the two incoming power lines originate from different regional substations. In contrast, in one scenario of dual loop power supply, the two incoming power lines come from different busbars within the same regional substation. Therefore, the "loop" in dual loop refers to the loop that emerges from the regional substation.
Dual power supply involves two independent power sources with different origins, and when one power source fails, the second one does not fail simultaneously, ensuring power supply to primary and secondary loads. On the other hand, dual loop generally refers to the end point, where one circuit is in operation while the other standby circuit is activated in case of a fault to supply power to the equipment. The two loops can be sourced from the same power supply or different power supplies.
Stay updated with Lisleapex by signing up for the newsletter


 Congratulations On Your Successful Submission
Congratulations On Your Successful Submission
 Submission Failure
Submission Failure