The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is a vital component within a vehicle’s engine management system, playing a critical role in regulating the engine's air-fuel mixture for optimal performance. By monitoring the position of the throttle valve, the TPS provides essential data to the engine control unit (ECU), ensuring precise control over engine power and efficiency. This article explores the TPS in depth, including its function, signs of failure, and diagnostic procedures. Whether you’re troubleshooting performance issues or performing routine maintenance, understanding the TPS and its operations is key to maintaining a smooth and efficient driving experience.
What is a TPS Sensor
A Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is a critical component in a vehicle's engine management system that monitors the position of the throttle valve. Typically mounted on the butterfly spindle of the throttle body, the TPS provides accurate readings of the throttle position. This data is crucial for the engine control module (ECM) to regulate the air intake and ensure optimal air-fuel mixture.

The throttle body, where the TPS is attached, has a silver-colored exterior and is connected by cables that link the sensor to the vehicle's electrical system. By using a scan tool, both the TPS and its circuitry can be diagnosed for any issues.
The primary function of the TPS is to allow the engine to maintain an appropriate air intake, which is essential for proper engine performance. When the gas pedal is pressed, the throttle valve opens, and the TPS adjusts the engine intake manifold accordingly. This adjustment is vital for maintaining smooth idling and acceleration.
In summary, the TPS plays a fundamental role in ensuring the correct mixture of air and fuel, contributing to the overall performance and power of the vehicle. If the TPS is damaged or malfunctioning, it is essential to replace it to restore the vehicle's optimal performance.
1) Location
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is typically mounted on the throttle body, which houses the throttle valve.
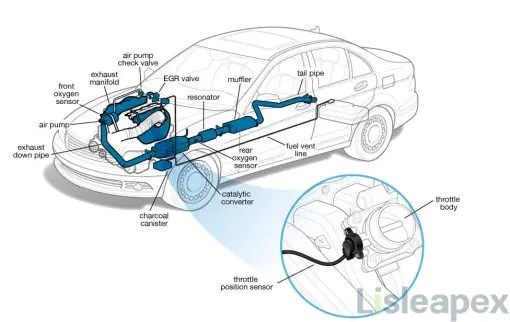
2) Types
Throttle position sensors come in three primary types, differentiated by their design characteristics:
- Closed Throttle Position Sensors: These sensors, often referred to simply as throttle position sensors, feature built-in end switches.
- Potentiometer Sensors: This type of TPS functions based on the principle of a potentiometer, providing variable resistance based on the throttle position.
- Hybrid Sensors: These sensors combine aspects of both closed throttle position sensors and potentiometer sensors, incorporating elements from each design for enhanced functionality.
What Does TPS (Throttle Position Sensor) Do?
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) plays a crucial role in a vehicle's engine management system by monitoring the position of the throttle valve (butterfly valve) and sending this data to the engine control unit (ECU). The sensor determines the position of the accelerator pedal based on how far it is pressed and measures the corresponding current generated.
The TPS regulates the amount of air entering the engine. When the throttle valve is fully open, a large volume of air flows into the engine; when the valve is closed, the air flow is minimal. The TPS provides this information to the ECU, which then calculates the appropriate amount of fuel to inject into the engine for optimal combustion.
The TPS is a potentiometer with three wires: a 5V power supply, a ground wire, and an output wire connected to the wiper of the potentiometer. This output signal is used by the ECU to adjust the fuel injection based on the throttle position. The TPS works in conjunction with other sensors, such as the mass airflow sensor and the RPM sensor, to ensure the correct air-fuel mixture for efficient engine performance.
When the accelerator pedal is pressed, the throttle valve opens, allowing more air to enter the engine. The TPS measures the amount of air and relays this data to the ECU, which adjusts the fuel injection accordingly. A properly functioning TPS ensures smooth acceleration, efficient engine operation, and optimal fuel economy.
If the TPS is faulty, the ECU cannot accurately determine the throttle position, leading to incorrect fuel-air mixture, poor fuel economy, and potential engine performance issues. Regular diagnostic checks using a scan tool can help identify and address TPS malfunctions to maintain vehicle performance.
How to Tell If a TPS Sensor is Bad?(Signs and Symptons)
A malfunctioning Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) can lead to several engine performance issues. Here are the common signs
Irregular Idle and Stalling:
- The engine idles too slowly or stalls completely.
- The idle is not smooth and fluctuates.
Erratic Acceleration:
- The vehicle accelerates inconsistently, either accelerating on its own or failing to accelerate when the pedal is pressed.
- Noticeable delays or sluggish response when accelerating.
Lack of Power:
- The car exhibits a clear lack of power despite pressing the accelerator.
Gear Shifting Issues:
- The transmission may fail to shift properly, leading to driving difficulties.
Check Engine Light (CEL):
- The CEL may illuminate, indicating a potential issue with the TPS.
Reduced Fuel Economy:
- A drop in fuel efficiency due to improper air-fuel mixture.
5 Ways to Diagnosing a Bad TPS
1. Use an OBD-II Scanner:

Connect a good OBD scan tool to your vehicle to check for specific trouble codes related to the TPS, such as P0120 or P0121.
2. Physical Inspection:
Visually inspect the TPS and its wiring for any visible signs of damage, wear, or corrosion.
3. Voltage Testing with a Multimeter:
Measure the voltage output of the TPS. The voltage should change smoothly as the throttle is moved. Sudden jumps or drops in voltage indicate a faulty sensor.

4. Resistance Testing:
Check the resistance across the TPS terminals. A high or infinite resistance reading can suggest a malfunction.
5. Live Data Monitoring:
Use a scan tool to monitor the live data from the TPS. Compare the sensor’s output with the actual throttle position. Any discrepancies point to a defective TPS.
How to Test TPS Sensor with Multimeter?

Step 1: Locate the Throttle Position Sensor
Begin by finding the throttle body, which is situated in the engine compartment and connected to the gasoline line. The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is mounted on the throttle body and has cables that lead to the engine control unit (ECU). Identifying the TPS involves locating this sensor on the throttle body, which controls the airflow into the engine.
Step 2: Identify the Wires
Once you have located the TPS, identify the wires connected to it. Typically, there are three types of wires: the ground wire, the power wire, and the signal wire. The ground wire is usually black, the power wire is red, and the signal wire may be a different color such as yellow, green, or blue. Knowing these wire colors helps in correctly connecting the multimeter.
Step 3: Test the Reference Voltage
Set your multimeter to the voltage (V) setting. To measure the reference voltage, connect the multimeter probes to the TPS wires: attach the negative probe to the ground wire and the positive probe to the power wire. A properly functioning TPS should display a reference voltage of approximately 5 volts. This reading confirms that the TPS is receiving the correct power supply from the ECU.
Step 4: Evaluate the Signal Voltage
To test the signal voltage, connect the multimeter probes differently: place the positive probe on the signal wire and the negative probe on the vehicle frame (ground). As you move the throttle, the signal voltage should change smoothly. At idle (closed throttle), the voltage should be around 0.5 volts, and it should rise progressively to about 4.5 volts when the throttle is fully open. Smooth and consistent changes in voltage indicate a properly functioning TPS.
Analyzing the Results
If the reference voltage is stable at 5 volts and the signal voltage changes smoothly in response to throttle movement, the TPS is likely working correctly. However, if you observe inconsistent, erratic, or out-of-range voltage readings, it suggests that the TPS may be faulty and should be replaced. Testing the TPS in this manner ensures accurate diagnostics and helps maintain optimal engine performance.
How to Check TPS Sensor Using a Scan Tool
A faulty Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) can trigger diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) ranging from P0120 to P0124. The most common code is P0122, which indicates a low input voltage from the TPS. Here’s a step-by-step guide to diagnosing a bad TPS using a scan tool:
Step 1: Pull Trouble Codes
Connect the Scan Tool:
Plug the scan tool into the vehicle's OBD-II port.
Turn the ignition to the "On" position (KOEO - Key On, Engine Off).
Read Trouble Codes:
Access the scan tool’s menu to read all stored trouble codes.
Look for TPS-related codes, such as P0120, P0121, P0122, P0123, and P0124.
If any TPS codes are present, proceed to the next step.
Step 2: Clear the Codes
Erase Trouble Codes:
Use the scan tool to clear all stored codes.
Ensure that the vehicle is in the KOEO state during this process.
Step 3: Perform a Driving Cycle
Start the Engine:
Disconnect the scan tool and start the engine.
Monitor the Check Engine Light (CEL):
If the CEL turns off, the issue may have been intermittent.
If the CEL remains on, conduct a 5 to 10-minute test drive.
Recheck Trouble Codes:
If the CEL comes back on during the test drive, reconnect the scan tool and read the codes again.
Confirm if TPS codes are still present before moving to the next step.
Step 4: Check Live Data
Access Live Data:
Reconnect the scan tool and switch the car to the KOEO mode.
Navigate to the live data section on the scan tool.
Lock the TPS data on the display screen.
Graph TPS Data:
If your scan tool supports live data graphing, use it to graph the TPS output.
Step 5: Analyze the Graph
Observe TPS Response:
Slowly press and release the accelerator pedal.
Monitor the TPS output graph. A healthy TPS will show a smooth, linear graph with a positive slope.
Identify Faulty Behavior:
Abrupt changes or irregularities in the graph indicate a faulty TPS.
Both sudden positive and negative slope changes suggest the sensor is malfunctioning.
Replace the TPS:
If the TPS is confirmed faulty, replace it with a new one.
You may need to perform a TPS relearn procedure using a scan tool with programming capabilities.
Avoid Cleaning the TPS:
Do not attempt to clean the TPS, as this can contaminate or damage the sensor.
Cleaning the throttle body is acceptable, but avoid contact with the TPS.
Cost Factors:
The cost of replacing a TPS varies based on the vehicle make and model.
If the sensor is easily accessible, the replacement cost (parts and labor) is typically under €500.
For sensors located in hard-to-reach areas, the cost can rise to €1000 or more due to increased labor.
How to Reset TPS Sensor
Resetting the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) can help recalibrate the sensor and ensure accurate throttle response. Here’s a simple procedure to reset the TPS:
Turn the Ignition On:

Insert the key into the ignition and turn it to the "On" position without starting the engine. This powers up the vehicle’s electrical system without engaging the engine.
Locate and Press the Reset Button:
Find the TPMS reset button, which is typically located underneath the steering wheel or near the dashboard. Press and hold the button until the indicator light associated with the tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) flashes three times. Release the button after the third flash.
Start the Engine:
Turn the ignition key to start the engine. This allows the TPS to begin its calibration process.
Allow the Sensor to Reset:
Let the engine run for approximately 20 minutes to allow the TPS to reset and recalibrate. During this time, the sensor will adjust itself based on the new throttle position data.
Conclusion
In summary, the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is crucial for accurate engine performance and fuel efficiency. Regular maintenance and timely diagnostics are essential to prevent issues related to a malfunctioning TPS. By understanding the sensor's role and the symptoms of potential faults, vehicle owners can take proactive steps to ensure their engine operates optimally. Whether through testing with a multimeter, using a scan tool for diagnostics, or performing a reset, addressing TPS-related problems promptly can enhance vehicle performance and longevity. Always consult professional guidance if uncertain about performing repairs to ensure the best outcomes for your vehicle.
Related Post
How Many Sensors in FBD Fluidized Bed Dryer 2023>>
How to Reset Crankshaft Position Sensor 2023>>
How to Trick a Mass Air Flow Sensor>>
ACS712 Current Sensor: Datasheet, Arduino and How to Use Guide>>
HMC2003 Honeywell 3-axis Magnetic Sensor Datasheet>>
FAQ
-
Can a faulty TPS affect engine performance?
Yes, a faulty TPS can lead to poor engine performance because the ECU relies on accurate throttle position data to adjust fuel and air mixtures and ignition timing.
-
How do you replace a TPS?
Replacing a TPS typically involves disconnecting the battery, removing the sensor's electrical connector, unscrewing the sensor from the throttle body, and installing the new sensor. Specific steps can vary by vehicle model.
-
Will a faulty TPS cause a check engine light?
Yes, a malfunctioning TPS can trigger the check engine light as the ECU detects irregular throttle position readings.
-
What are common diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to TPS?
Common DTCs include P0120 (Throttle Position Sensor/Switch A Circuit Malfunction), P0121 (TPS/Switch A Circuit Range/Performance Problem), and P0122 (TPS/Switch A Circuit Low Input).
-
Is the TPS the same as the accelerator pedal position sensor?
No, while both sensors measure throttle position, the accelerator pedal position sensor is located at the pedal and measures the driver's input, whereas the TPS is located on the throttle body and measures the actual position of the throttle valve.
-
Can cleaning the TPS solve issues?
Sometimes, cleaning the TPS and throttle body can resolve issues caused by dirt or carbon build-up. However, if the sensor is faulty, it will need to be replaced.
Stay updated with Lisleapex by signing up for the newsletter


 Congratulations On Your Successful Submission
Congratulations On Your Successful Submission
 Submission Failure
Submission Failure